VALIDATION OF DISINFECTANT EFFICACY
Developing a local SOP is giving a detailed description of the requirements for disinfectant efficacy testing and validation of the method is extremely important, for which various methods can be used, which are given below.
Test Method – The Time Contact Test
The test will demonstrate the ability of the disinfectant to kill or inhibit a large population of organisms within a specified contact time period. There are two methods which can be employed for the time contact test
- a) The Dilution-Neutralization method.
- b) The Membrane Filtration method.
The method of choice is the Dilution-Neutralization method. This method should be used where possible. In cases where the disinfectant is shown to resist dilution Neutralization, then the membrane filtration method may be employed.
Preparation Of Working Cultures
The working cultures should be prepared using the following guidelines:- For bacterial cultures subculture the organism onto a suitable media e.g. Tryptone Soya Agar ( TSA) and incubate at 30 ñ 35°C as necessary. For the Fungal isolates the organism should be sub cultured onto a media such as Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA) and Incubated at 20 ñ 25°C as necessary. For Moulds the plates should be incubated for up to 10 days to allow adequate sporulation to occur. The Test suspensions should be prepared using a suitable diluent such as 0.1% peptone solution. A suitable volume is 10-20mls. The media detailed above should be used as guideline. Alternative diluents or growth media may be used according to local procedures. The test suspensions MUST be adjusted to contain at least the following numbers of viable cells:-
Bacterial Test suspension = >1.0 x 108 cfu/ml.
Fungal Test suspension = >1.0 x 107 cfu/ml.
Bacterial Spore Test Suspension = >1.0 x 106 cfu/ml.
N.B Validation should be carried out beforehand to determine the required turbidity for the suspension. The test suspension MUST then be diluted to the following log dilutions:-
Bacterial Test Suspension = Dilute to 10-7.
Fungal Test Suspension = Dilute to 10-6.
Bacterial Spore Test Suspension = Dilute to 10-5.
Pour Plates should be prepared from the last two dilutions e.g. 10-5 and 10-6 for Fungal Test suspensions. Growth media may be used according to local procedures e.g. Tryptone Soya Agar. Incubate the plates at 30 ñ 35°C for bacteria and bacterial spores. Incubate the fungal test plates at 20 ñ, 25°C to achieve adequate growth for quantification. Determine the number of cfu/ml (N) in the Bacterial/Fungal Test suspension.
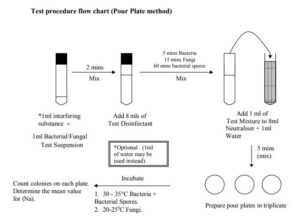
The Dilution-Neutralization Method
Prior to testing allow all reagents to equilibrate to ambient temperature. This should normally be 20 ñ 25°C. Pipette 1 ml of Interfering substance* into a sterile empty test tube if necessary. Add 1ml of the Test Suspension prepared as detailed above. Allow the mixture to stand for 2 mins. * Interfering substance such as bovine albumin solution may be employed in the test to simulate organic soiling. The amount used will depend on the levels of contamination that would be expected when the disinfectant is in routine use. A guideline for simulation of dirty conditions is a final concentration 3g/litre At the end of this time add 8ml of the disinfectant test solution and mix thoroughly. Immediately start the timer/stopwatch and allow to stand for the required contact time. This should be a maximum of 5 mins for bacteria. The contact time for fungal isolates will be 15mins and 60 mins for bacterial spores. Just before the end of the contact time mix the suspension thoroughly. Immediately pipette 1ml of the test solution into a sterile tube containing 8ml of a suitable neutraliser and 1 ml of sterile distilled water. Mix the solution thoroughly and allow to stand for 5 mins. Prepare Triplicate 1ml pour plates from the neutralised mixture. Incubate the test plates using the guidelines stated previous Count the number of colonies on each test plate. Determine the Mean number of cfu/ml (Na) in the test mixture. This is calculated as follows:-
Mean number of cfu/ml (Na) = V x D x N C Where:-
C = Total number of colonies counted on all of the plates.
V = Sample volume used to prepare the plates. For the Pour plate method this will be 1ml. For the membrane filtration method this will be 0.1ml.
D = The dilution factor for the dilution taken into account. For the Pour plate method this will be 0.1. For the membrane filtration method this will be 1.
N = The number of plates taken into account.
Determine the mean Logarithmic reduction for the viable count in the test mixture:- Mean logarithmic reduction = Log10 (N x 0.1)ñ Log10 Na
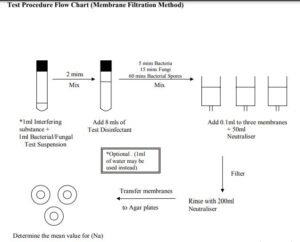
The Membrane Filtration Method.
Repeat the steps in the procedure for the dilution Neutralization method up to the test sample inoculation. Just before the end of the contact time mix the suspension thoroughly. Immediately pipette three 0.1ml aliquots into separate membrane filters containing 50mls of neutralizer. Filter the contents immediately. Rinse the membrane with 200ml of neutralizer Transfer the membranes to suitable agar media plates depending on the isolate. Determine the Mean number of cfu/ml (Na) in the test mixture using the guidelines stated previously Test Controls: Validation Of The Dilution-Neutralization Method.
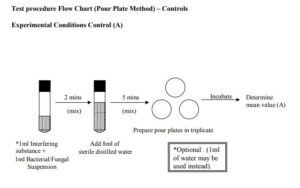
Experimental Conditions Control
This is carried out to demonstrate that the interfering substance solution does not interfere with the growth of the challenge organism.
Prepare a suspension of the challenge organism in the diluent solution containing the following number of cfu/ml (Nv). For Bacteria, Bacterial spores and Fungal suspensions, Nv = 6.0 x 102 ñ 5.0 x 103 cfu/ml. The dilutions prepared to determine the inoculum count can be used for the suspensions.
For Bacterial suspensions use: The 10-5 dilution
For Fungal Suspensions use: The 10-4 dilution
For Bacterial Spore Suspensions use: The 10-3 dilution
The value of Nv can be determined from the value of N calculated previously. This is achieved by taking into account the Log dilution of the suspension to be used for the controls. Place 1ml of the suspension into a sterile tube and then add 1ml of the interfering substance solution. Mix the contents thoroughly and allow to stand for 2 minutes. Add 8ml of sterile distilled water and mix the suspension. Allow the contents to stand for 5 minutes and then mix thoroughly. Prepare triplicate 1ml pour plates as detailed previously. Determine the number of colonies on each plate to give the mean value.(A)
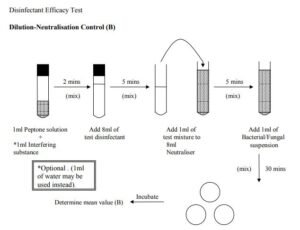
B) Dilution-Neutralization Control
Dilution Neutralization/Filtration Test Control ñ This control is carried out to demonstrate that the effect of the disinfectant has been eliminated. The challenge organisms will be introduced after the dilution Neutralization or membrane filtration step involving the disinfectant has taken place. Place 1ml of the interfering substance solution prepared previously into a sterile tube and add 1 ml of the diluent solution. Add 8ml of the disinfectant and mix thoroughly, allow to stand for 2 mins. After this equilibration period add 1ml of the mixture to 8ml of neutralizer solution and 1 ml of distilled water in a sterile tube. Mix the contents thoroughly. Allow to stand for 5mins. Add 1 ml of the suspension detailed above and mix thoroughly. Allow the mixture to stand for a minimum of 30mins. When this time period is over mix the contents and prepare triplicate 1ml pour plates as detailed previously. Determine the number of colonies on each plate and calculate the mean value (B).
Test Controls: Validation of The Membrane Filtration Method
The suspension to be used for the test is detailed in the previous sections,
A) Experimental Conditions Control Note: If the interfering substance is not employed in the test then it would not be necessary to perform this control. Add 1ml of the mixture to three membranes containing 50ml of Neutraliser. Immediately filter the contents and then rinse with 200ml of Neutraliser Transfer the membranes to separate agar plates and incubate as detailed previously. Count the number of colonies on each plate. Determine the mean value (A).
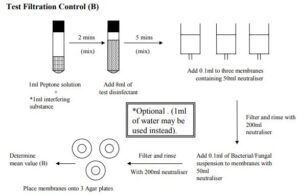
B) Filtration Test Control: The suspension to be used for the test is detailed in the previous sections Place 1ml of the interfering substance solution into a sterile tube and add 1 ml of diluent solution. Add 8ml of the disinfectant and mix thoroughly, Allow to stand for 2 mins. Add 50ml of neutraliser to three membrane filters and then add 0.1ml of the mixture to the filter unit. Immediately filter the contents and rinse with 200ml of Neutraliser. Add a further 50ml of Neutraliser to the filter and add 0.1ml of the isolate suspension. Filter the contents and rinse with 200ml of Neutraliser. Place the membranes onto agar plates as necessary and incubate as necessary. Determine the number of colonies one each plate and calculate the mean value (B).
Acceptance Criteria
The isolate test suspension viable count (N) is as follows:
Bacterial Test suspension = > 1.0 x 108 cfu/ml.
Fungal Test suspension = > 1.0 x 107 cfu/ml.
Bacterial Spore Test Suspension = >1.0 x 106 cfu/ml.
In cases where the count exceeds this value a review should be undertaken to determine whether this has any impact on the validity of the test result. The Dilution-Neutralization and Membrane Filtration test acceptance criteria are:
A log 5 reduction for bacteria within 5 minutes.
A log 4 reduction for fungi within 15 minutes.
A log 3 reduction for bacterial spores within 60 minutes.
Test controls The isolate suspension viable count (Nv) = 6.0 x102 ñ 5.0 x 103 . The Mean value for the experimental conditions control (A) = ≥70% Nv. The mean value for the dilution-Neutralization or filtration test control (B) = ≥70% Nv. Where a disinfectant does not meet this acceptance criteria further work using a higher disinfectant concentration or longer contact time may be required to verify results before the disinfectant is rejected or accepted for use.
Detailed illustration of test procedures is given below.